Coal
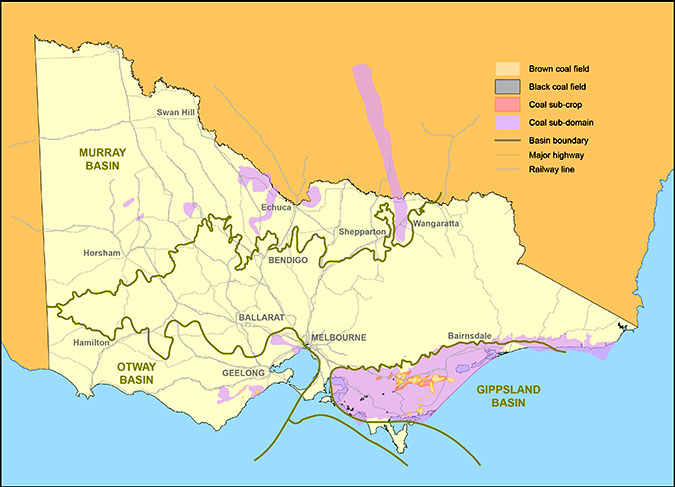
Victoria has an estimated 430 billion tonnes of brown coal in situ. More than 80 per cent of this brown coal (also called lignite) is located in the Gippsland Basin, off the South-East coast of Victoria.
Brown coal deposits
Brown coal seams in the Latrobe Valley are up to 100 metres thick with multiple seams often giving nearly continuous thickness of up to 230 metres. Seams are typically located under only 10-20 metres of overburden.
Therefore, open-cut mining has been used to extract brown coal in Victoria. The Loy Yang and Yallourn mines in the Latrobe Valley produce the majority of brown coal.
While the majority of coal in the Latrobe Valley is brown coal, an estimated 6.8 million tonnes of black or bituminous coal is located in western Gippsland. These deposits are high volatile black coal with medium ash and moisture content.
Beyond the Gippsland Basin, other brown coal deposits can be found in the Otway Basin (mainly within the Bacchus Marsh, Altona and the Anglesea coalfields) and across the Murray Basin.
Brown coal basics
Victoria’s lignite is typically low in ash, sulphur, heavy metals and nitrogen. However, its high moisture content - which ranges from 48-70 per cent - reduces its effective energy content (average 8.6 MJ/kg on a net wet basis or 26.6 MJ/kg on a gross dry basis).
Typical Characteristics of Victorian Lignite Brown Coal
| Energy value (net wet) | 5.8 to 11.5 MJ/kg |
| Energy value (gross dry) | 25 to 29 MJ/kg |
| Overburden thickness | 10 to 20 metres |
| Strip ratio (coal: overburden) | 0.5 to 5:1 |
| Water | 48 to 70% |
| Carbon | 65 to 70% |
| Oxygen | 25 to 30% |
| Hydrogen | 4 to 5.5% |
| Ash | <4% |
| Nitrogen | <1% |
| Sulphur | <1% |
Low rank coal comparative
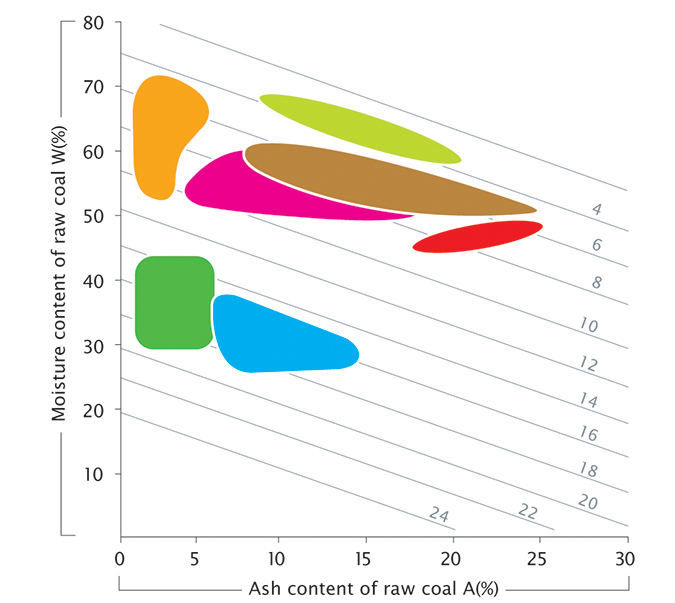
| Key | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Latrobe Valley | Puentes Spain | ||
| Megalopolis Greece | Dakota Texas U.S.A | ||
| Ptolemais Greece | Indonesian Low Rank | ||
| Neurath D, Germany | __ | Net Specific Energy (MJ/kg) | |
Source: Allardice Consulting Ltd
Page last updated: 19 Jun 2024